What is a payment gateway and how does it work?
The checkout page is an essential part of every online business. Companies can significantly improve their conversion rates by offering convenient payment options to their customers. By choosing a reliable payment gateway, merchants can grow their businesses and focus on their core business rather than figuring out how to collect payments.
This extensive guide explains what a payment gateway is, how it works, and what to consider when choosing the best solution for your company.
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is an infrastructure that allows collecting and transferring payment data from the point of interaction (PI) to the payment processor. The point of interaction can be a website, a mobile device, or a terminal.
In simple terms, a payment gateway allows merchants to accept online payments from their consumers.
How does the payment gateway work?
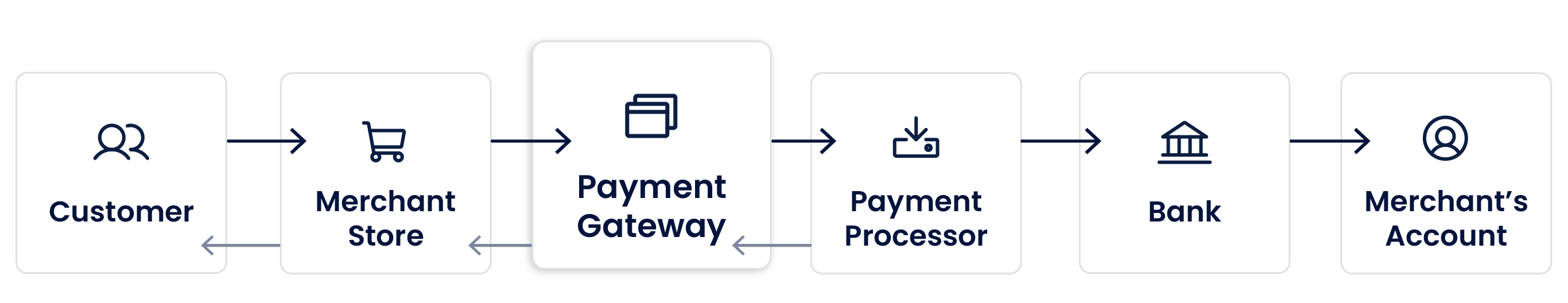
Online transactions through a payment gateway include a number of stakeholders. These are the main ones:
- Business — any type of entity selling goods or services.
- Consumer — the payer who makes a purchase.
- Issuing bank — a financial institution that holds the consumer’s account.
- Acquiring bank — a financial institution holding the merchant’s agreement and account.
- Issuer processor — technologic partner of the issuing bank that handles most of the tech functions like pin validation (pinblock), 3D secure (ACS), etc.
- Card schemes networks — debit/credit card processing companies such as Visa, Mastercard, etc.
- Acquirer processor — technologic partner of the acquiring bank, usually responsible for the payment gateway and POS processing.
Here’s an example of how the payment gateway may work:
- A consumer initiates a payment by making a purchase on a merchant’s website.
- The gateway on the merchant website sends encrypted payment card information to the card network, via the acquirer processor, on behalf of the acquiring bank.
- Based on the card details, the card network sends the transaction to the issuing bank via issuer processors to authenticate users (in case of 3D secure) to ensure the funds are available and, depending on the risk rules, if the issuer approves the transaction.
- The issuer approves or declines the transaction and sends the response to the gateway via the issuer processor, card network and acquirer processor.
- If the transaction is approved, the card network settles the funds with the acquiring bank by moving the funds from the consumer's bank account to the acquiring bank. The acquiring bank then moves the money to the merchant's account, according to contract rules and an agreed rolling reserve.
This flow can be shortened by eliminating the issuer processor, acquiring processor and card networks. PSD2 made it possible for licensed payment service providers to offer account-to-account (A2A) payments. These payments enable direct transactions from the consumer’s bank account to the merchant’s account, skipping the acquirers, processors and card networks. A2A payments cost less for merchants because they don’t have to pay any fees related to card processing and don’t have to have rolling reserves on acquirers.
Types of payment gateways
Payment gateways come in three main types:
Redirect
A redirect payment gateway takes the consumer to the payment processor to proceed with the payment. A new window opens up in most cases, and the consumer can enter their payment details there. Once the payment is completed, the consumer is redirected back to the merchant's page.
This type of payment processing is the most secure and convenient, but because of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) certification, the gateway provider cannot let the merchant have full control over the client’s checkout experience.
Self-hosted
A self-hosted payment gateway, also known as an on-site payment gateway, allows the consumer to pay without leaving the merchant’s site. All the checkout happens on the merchant’s website or a mobile app, giving the merchant full control of the payment experience.
In this case, the merchant needs to hold a PCI DSS certification in order to collect all the payment data encrypted and sent from the merchant’s site to the gateway for authorisation and further processing.
Hosted
A hosted payment gateway, or an API-hosted payment gateway, is a mix of redirect and self-hosted payments. In this case, all the payment details are entered on the merchant’s website using an API. The APIs offer a fully customisable checkout experience with maximum security.
API-hosted gateways can be integrated into mobile devices for in-app payments. This type of payment solution ensures both high-level security and the best customer checkout experience. Merchants' websites have to be certified by PCI DSS.
What is the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
The main difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor is their role in the payment process. A payment gateway is an infrastructure that ensures the communication of payment details between merchants and payment processors. The payment processor is the entity responsible for moving the funds between the consumer and merchant accounts.
What are the advantages of a payment gateway?
Using a payment gateway for a business may bring many benefits. Here are the main advantages:
Security
Payment gateways comply with various security requirements, including PCI DSS certification, and use features that ensure fraud protection. For example, kevin. provides a payment solution that is PSD2 and GDPR compliant and uses high-standard security features that help protect against payment fraud.
Speed
Transferring payments from the consumer’s to the merchant’s bank account manually is inconvenient and slow. Payment gateways provide fast transfers that are easy to use for both merchants and their customers.
Customer experience
17% of online shoppers abandon their carts if they find the checkout process too long or complicated. A well-chosen payment gateway can reduce abandoned carts by 50%, ensure a simple and convenient checkout experience, and increase consumer conversion rates.
Cost
Some payment initiation service (PIS) providers, such as kevin., offer account-to-account payments that eliminate card processors and card networks from the payment process. This reduces the payment costs as merchants don’t have to pay card processing fees.
Easy scaling
Depending on a payment solution, it can help you scale your business and expand internationally. For example, kevin. allows merchants to accept payments from 27 countries across Europe with no additional cost, which significantly increases companies’ customer base, even if it’s a local business.
Are payment gateways secure?
Payment gateways have various security standards that they comply with. These are the most common ones:
Encryption
All the data that travels through payment gateways is usually encrypted. This means that even if someone leaked sensitive information, such as a card or bank details, it wouldn’t be of any use to anyone. Only authorised parties have access to the encryption codes and can read the data.
PCI compliance certification
The PCI DSS includes a security checklist that helps prevent or reduce fraud. Some payment providers have the PCI compliance certificate. Small and medium businesses that partner with a PCI DSS compliant payment service provider don't need to undergo an on-site audit by a qualified security assessor (QSA).
Strong customer authentication (SCA) and PSD2
PSD2 regulates electronic payments in Europe, and strong customer authentication (SCA) is a security requirement for all companies that deal with online payments on the continent. This means that all the payment service providers in the EU and EEA have to be PSD2 and SCA compliant.
Examples of payment gateways
Some of the most popular payment gateways are PayPal, Stripe, and Worldpay.
However, more and more promising new payment providers are joining the market and offering innovative solutions. For example, kevin. is a fast-rising payments infrastructure that offers a payment gateway with the same great features as the most prominent players in the industry for a fair price.
How to choose an online payment gateway?
While the market is filled with various payment service providers, choosing the right payment gateway isn’t an easy task. Considering the following points may help you make the right choice:
Coverage
Depending on the size of your business and future expansion plans, choose a payment service provider that has broad coverage. For example, kevin. has integrated most banks from 27 ES and EEA countries, which means you can easily accept payments from 350M consumers all across Europe.
Security
Choose a third-party payment gateway provider that is compliant with the highest security standards. Find out about your chosen provider’s security features and make sure to ask about their compliance.
Compatibility with your e-commerce site
Some solutions can be integrated with various e-commerce platforms or plugins, such as WooCommerce, Shopify, etc. Find out which gateway is most compatible with your e-commerce site’s structure.
Budget
The cost of payment solutions can widely vary. Some providers charge a set fee for every transaction, while others also include set up and administration fees. Chargebacks may also come with an additional fee.
Payment methods
Different providers may support different payment methods. Most of them accept bank payments and card payments, as well as a number of other options. Make sure your chosen provider supports the payment methods that are most convenient for your consumers.
How much does a payment gateway cost?
Most payment gateways charge a percentage or a set fee per transaction. Others offer a monthly subscription. Smaller companies with fewer sales tend to choose to pay per transaction.
Some providers charge for setup and administration and may ask companies to pay for additional features. In most cases, sales reports, security features, and integrations with third-party e-commerce platforms are included in the price.
How to integrate a payment gateway into a website?
The exact integration may depend on the service provider and the type of gateway you choose, but here are the general steps you may expect.
For example, to integrate a hosted gateway, connect your website to the gateway and obtain an SSL certificate. Contact your payment provider to get the gateway’s credentials, such as the merchant’s ID, MWS key, and secret key.
kevin. payment gateway integration is straightforward and well-documented. You can get familiar with the public documentation for reference.
Benefits and features of kevin. e-commerce payment gateway
kevin. offers a convenient and secure payment gateway that brings a number of benefits for e-commerce companies. Here are some of the features:
One-click payments
Companies can boost their conversion rates with kevin. one-click payment feature. Bank account linking enables consumers to pay directly from their bank account with just one click.
Card redirect feature
This feature automatically redirects consumers to finish the payment in their bank account rather than pay with a card. Card redirect reduces transaction costs for merchants and improves the checkout time for consumers.
Easy integration
kevin. payment gateway can be easily integrated with the most popular e-commerce platforms such as WooCommerce, Prestashop, and many others. If you’re looking for a custom solution, kevin. can offer that, too.
Transparent pricing
kevin. charges a small amount for every successful transaction and has no hidden fees.
Conclusion
A payment gateway is essential for companies that want to offer secure and convenient payments for their customers. Various payment solutions can provide different payment methods that quickly collect payments from consumers in various locations and bring other benefits.
kevin. is a payment service provider with an innovative approach. It offers various features that help companies save on transaction costs. Get in touch and find out what kevin. can offer for your business.