What is a payment service provider (PSP)?
Payment service provider (PSP), payment solution provider, or merchant services provider are synonyms. They describe a financial institution authorized to process money transactions between merchants and their customers. In other words, PSPs are third-party providers that enable companies to accept payments from their clients in a convenient way.
PSPs are links between merchants, acquiring banks, and payment card networks involved in payment transactions. Signing up with a PSP allows merchants to accept payments globally without having to open separate companies in different countries and set up merchant accounts.
While working with PSPs has a lot of advantages, choosing the right one may be a challenge. This article will explain how PSPs work, what benefits they provide, and how to pick the best payment provider for your business.
What are payment service providers (PSPs)?
Payment service providers (PSPs) are regulated digital financial transaction facilitators. They act as intermediaries between merchants or other companies collecting payments and their consumers. PSPs provide various services, such as payment processing, currency conversion, and fraud prevention. They help companies accept online payments from their consumers.
PSPs can integrate with various payment methods and enable companies to accept payments through multiple channels, such as debit or credit cards, e-wallets, direct bank transfers, etc. Payment service providers also take care of technical and regulatory compliance related to payment processing, such as data security, anti-money laundering regulations, and more.
PSPs are an integral part of the entire digital payment ecosystem, enabling merchants and other businesses to accept payments from consumers all over the world.
How do payment service providers (PSPs) work?
Setting up an e-commerce business or any other company that accepts payments for goods or services requires a payment solution. It can be a point-of-sale (POS), mobile in-app payment solution, a payment gateway, or a combination thereof. Payment service providers cover the entire payment flow and enable merchants to accept various payment methods, such as bank card payments, bank account transfers, etc.
In simple terms, payment solution providers gather all the relevant financial parties together to ensure smooth transactions between merchants and buyers. This includes the buyer, merchant, card networks, banks or other financial institutions.
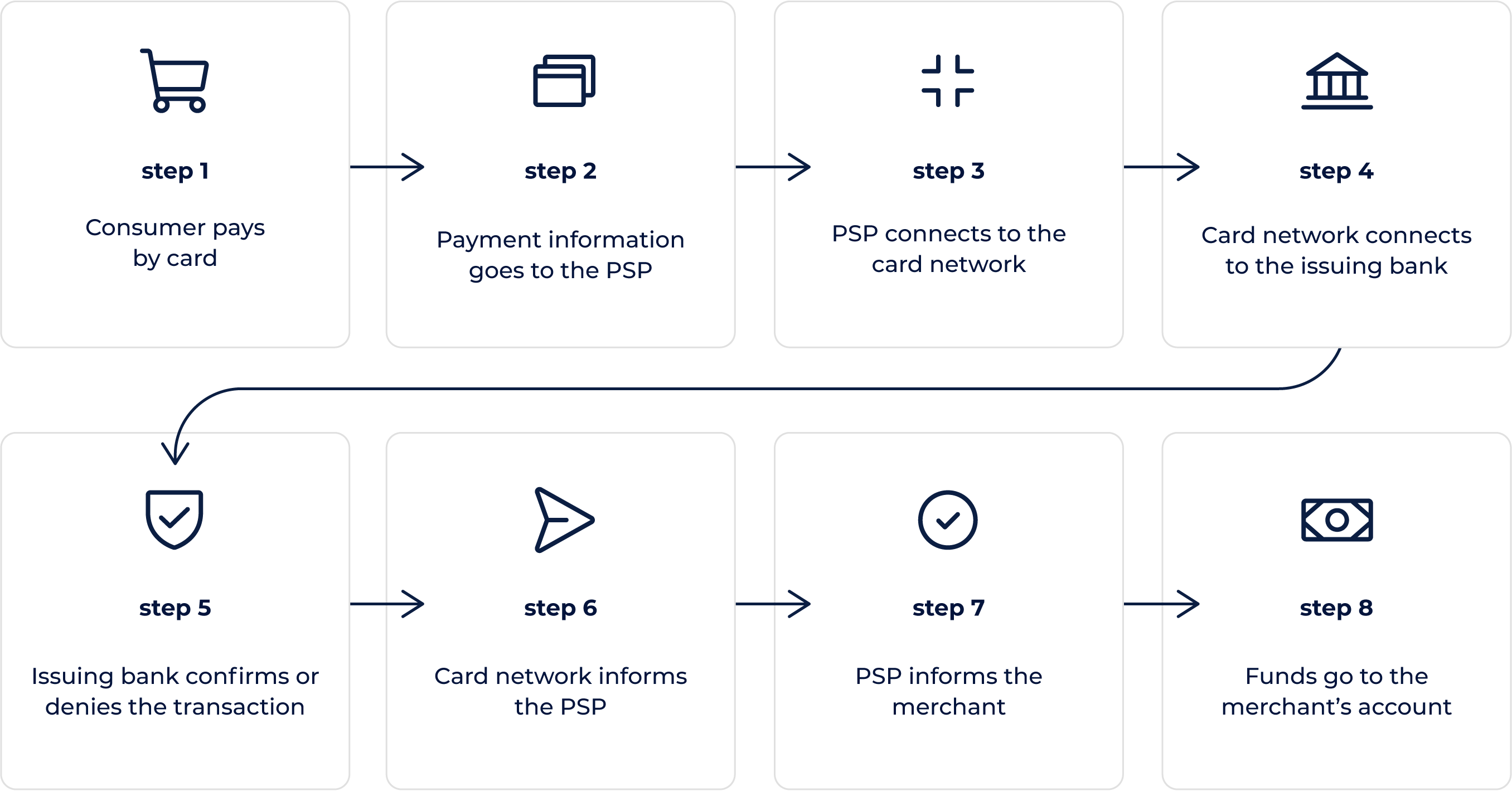
Each payment goes through three main steps: payment initiation, authorization, and transfer. Here’s an example of what online card transaction processing may look like:
1. A buyer picks goods or services from a merchant’s site and chooses to pay with a card.
2. The merchant’s installed payment gateway software sends the payment information to the PSP.
3. The PSP, via an acquiring bank, identifies the card network and connects to it on the merchant’s behalf.
4. The card network reports the transaction to the issuing bank.
5. The issuing bank runs a security check and sends an approval or denial code to the card network.
6. The card network, via the acquiring bank, sends the approval or denial information to the PSP.
7. The PSP transfers the same message to the merchant and displays it to the buyer.
8. If the transaction has been approved, the funds are transferred to the merchant’s account, based on the agreement with the PSP or the acquiring bank.
The processing flow may seem like a long process at first sight, but it only takes a few seconds in practice. PSPs can integrate with partners that offer various payment methods. For example, kevin. offers to bypass the card networks and enable buyers to pay directly from their bank accounts. Account to account payments speed up the transaction process, by eliminating unnecessary intermediaries while increasing security and reducing transaction costs.
What are the differences between payment service providers and payment gateways?
To understand the main differences between PSPs and payment gateways, here are the definitions of each term:
A payment gateway is a technology that helps merchants initiate transactions for different payment methods. It transfers data from the point of entry to the PSP or acquiring bank. The entry point can be an in-store POS terminal, a website, or a mobile device.
A payment service provider is a financial institution that processes the transaction. The PSP receives the transaction initiation request via the payment gateway.
While PSPs and payment gateways are essential in transaction processing, they play entirely different roles.
What are the differences between merchant accounts and payment service providers?
A merchant account is a special online account that merchants can set up and use to accept online payments. All the digital payments from the buyers end up in the merchant’s account. Each merchant account will have an assigned Merchant ID (MID) and, typically, is also assigned a Merchant Category Code (MCC). The MCC classifies a business by the type of products or services it provides.
PSPs manage one merchant account under a single MID per MCC and create sub-accounts for different merchants. Integrating with a PSP is much quicker than opening a merchant account.
Companies that open a merchant account still need to get a payment gateway to be able to accept payments online. Meanwhile, most PSPs cover the entire transaction processing, including the payment gateway.
What are the examples of payment service providers?
Some of the most popular and widely known PSPs are:
- PayPal
- Stripe
- Adyen
In some countries local PSPs are more popular than the big names. To find the best PSPs for their case, businesses should consider the needs of their consumers, integration, and coverage, among other features.
Benefits of payment service providers
Partnering with a payment service provider can bring a number of benefits to merchants. To provide a wholesome view, here are the main pros of PSPs:
1. Convenience
A payment service provider covers the entire payment process, so you don’t have to outsource different services for your business. This is convenient, cost-efficient, and more secure than working with multiple third-party providers to cover the entire payment flow.
2. Security
PSPs are regulated and comply with the latest requirements, including PCI DSS and the PSD2 directive. This ensures secure financial transactions and also helps businesses. Without a compliant PSP, your business would have to take care of all the compliance-related matters that affect payment processing.
3. Multiple payment methods
PSPs integrate with different payment methods, and offering payment methods that clients want can increase conversion rates and reduce abandoned cars. From the business perspective, you should know which payment options are the most popular among your customers, and a PSP can ensure this payment method appears at the checkout.
4. Conversions
A convenient checkout with multiple payment methods can increase conversion rates. Suspicious or complicated checkouts can drive consumers away. Statistics show that 18% of shoppers would abandon their carts if they found the checkout suspicious. 17% of consumers will leave if the payment process is complicated.
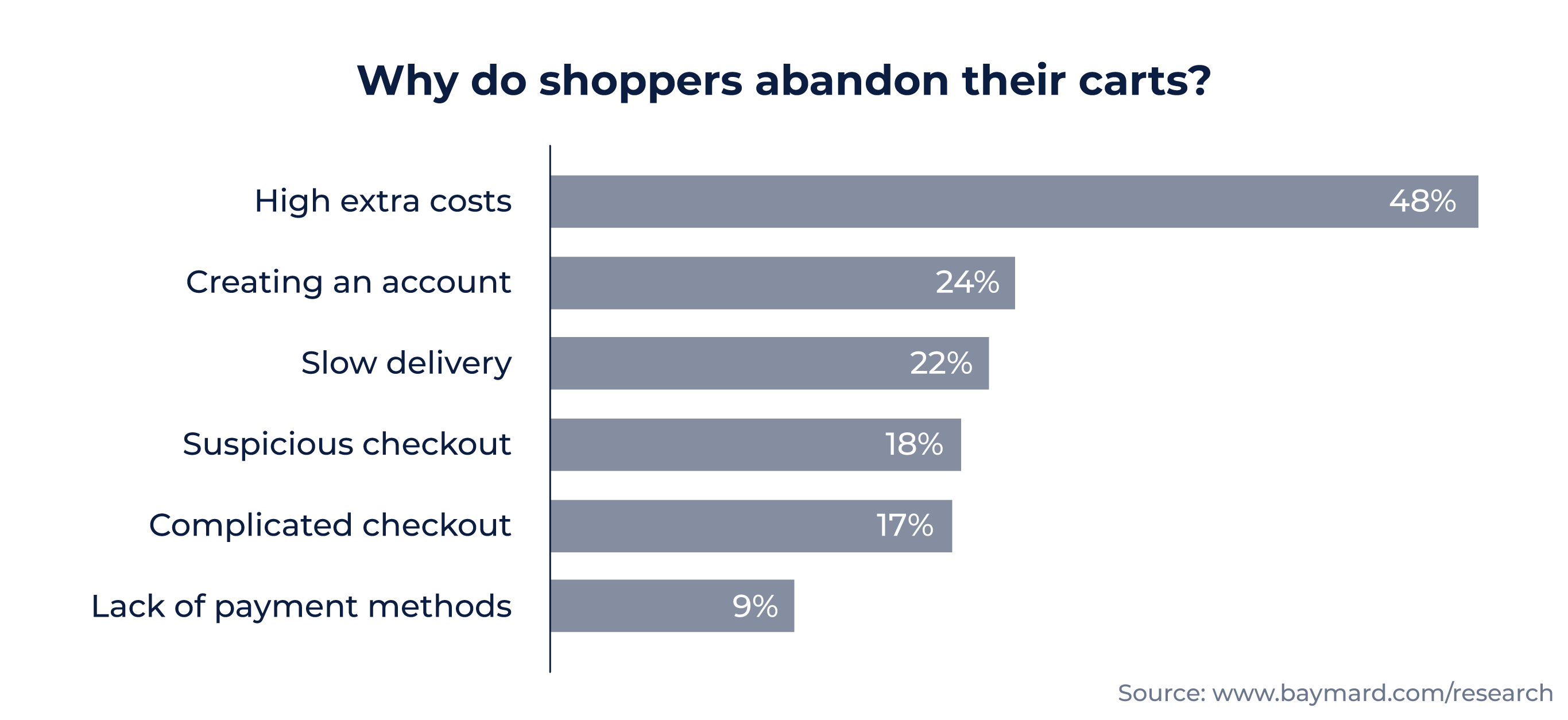
A payment service provider can ensure that the checkout process is smooth for your customers.
5. Integration
Integrating with a PSP can be quick and easy. Different PSPs offer various integration methods but in most cases, they’re simple and straightforward. Some providers only ask to integrate a single line of code. This means that merchants don’t need a dedicated team of developers to work on payment integrations.
How to choose a payment service provider?
Open banking has opened the door for innovative financial institutions to join the market that legacy banks have long ruled. Since then, many prospective financial players have entered the market and introduced payment features that benefit merchants and consumers.
Choosing the best payment service provider can be challenging, so we listed a few things companies should consider:
Security features
PSPs should ensure robust payment security. Some PSPs are compliant with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Selecting a PCI DSS compliant PSP means that merchants can save time and money because it reduces merchants’ PCI compliance scope.
Consider PSPs that can ensure secure data storage and have advanced fraud protection features in place.
Flexibility
If you’re operating a business with unconventional needs, you’ll need a PSP that can accommodate you. A customisable user interface for mobile applications, flexible pricing for companies with unique business models, and reliable customer support around the clock are some of the requirements to consider when choosing a PSP.
Coverage
Partnering with a PSP that offers a wide country coverage makes it easy for merchants to scale their businesses. Extensive coverage enables consumers to pay for goods and services via their local bank, even if they purchase goods from foreign e-commerce businesses. Consumers often abandon their shopping carts if they can’t find a suitable payment option, so offering their local payment method may increase conversion rates.
kevin. — an advanced partner for payment service providers
Payment service providers can partner up with kevin. to offer even more payment methods to their clients. kevin. has a well-developed infrastructure based on open banking, which allows PSPs to expand their services. If you’re a business and you’d like your PSP to offer the features that kevin. provides, let us know and we’ll approach your PSP for a partnership.