Payment tokenization explained: all you need to know
Data breaches and cyberattacks are a common threat to online businesses. When dealing with digital payments, there is an increased risk of these threats. However, tokens can be the answer to reducing the risk of online payment fraud.
This guide will help to learn about payment tokenization and the benefits it can bring to various businesses. Read on to find out about different types of tokenization and how this security feature differs from encryption.
What is payment tokenization?
Payment tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive information with non-sensitive data. Companies that deal with payments use tokens to securely transfer sensitive data by replacing it with a unique string of numbers and letters. These numbers cannot be tracked to the original data without having certain keys, which are held separately from the tokens and cannot be accessed by unauthorised users.
How does tokenization work in payments?
Payment tokens help securely identify clients and are used by e-commerce merchants and other companies that require the transfer of sensitive information about their consumers. It’s important to note that tokens itself don’t contain sensitive consumer information. Their role is more like a map’s - to explain where the consumer’s bank is storing such information within their systems.
For example, kevin. uses secure JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) to transfer banking data to merchants for open banking services, such as payment initiation services (PIS) and account linking. Instead of exchanging sensitive information, kevin. provides merchants with secure tokens, which are used to identify users and exchange the information needed for PIS.
The account linking feature used at kevin. enables consumers to link their bank account to the merchant’s platform and pay for goods and services with a single click. Once the accounts are linked, the merchant and payment initiation service provider (PISP) exchange secure tokens instead of transferring sensitive information for initiating payments.
These tokens enable merchants and the PISP to identify the consumer without requesting the same payment information from the consumer again for every payment.
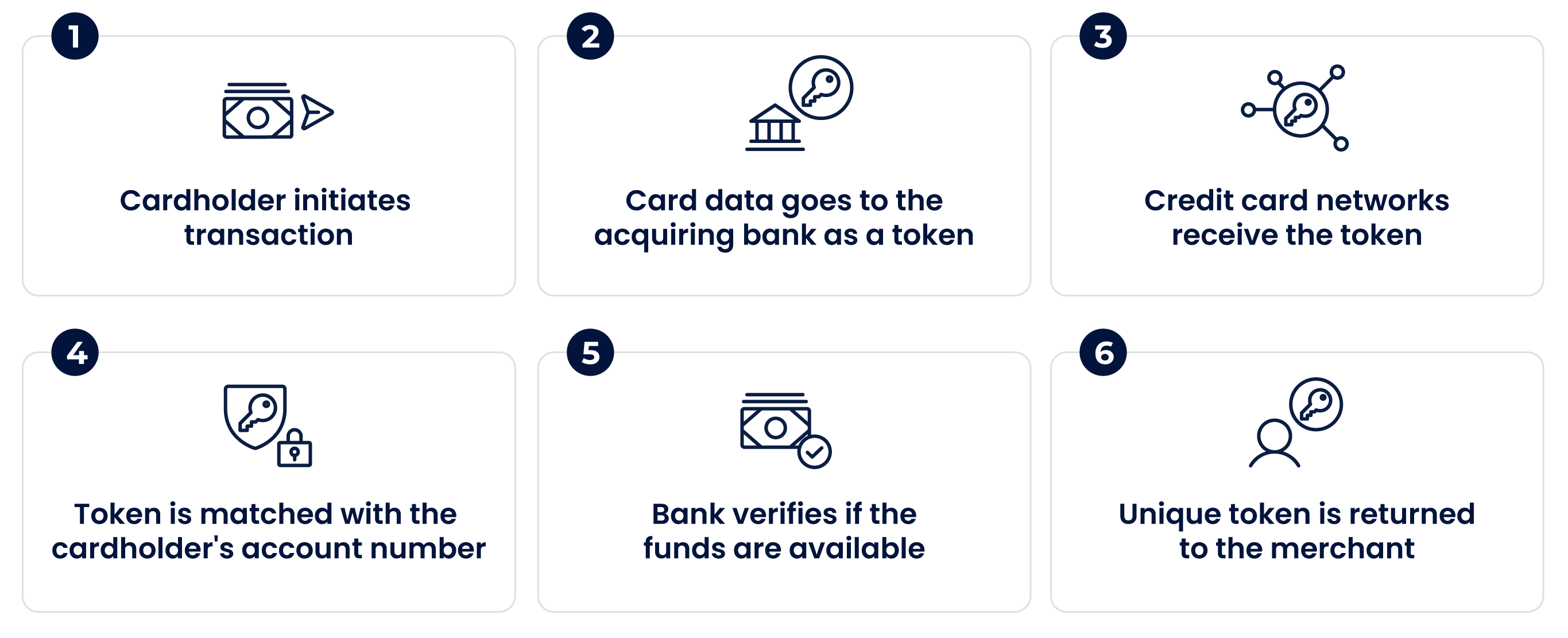
Various payment service providers also use tokens to securely transfer card data for online payments. A tokenized bank card transaction may look like this:
- The cardholder initiates a purchase transaction and enters their card details on the merchant’s site.
- The card data is replaced with a string of random numbers (a token) and goes to the merchant’s acquiring bank.
- The acquiring bank transmits the token to the card schemes for authorisation.
- When authorised, the cardholder’s data is stored in the bank’s virtual vaults. The token is matched to the cardholder’s bank account number.
- The bank verifies whether the required funds are available and confirms or rejects the transaction.
- If the transaction is confirmed, a unique token is returned to the merchant for this current and future transactions.
All of these steps happen in the back end of the systems, which means the user experience isn’t impacted by the tokenization process.
Examples of payment tokenization
Payment tokenization comes in three main forms for different use cases:
Card-on-file
A bank card or primary account number (PAN) is converted into a unique code and stored in a secure merchant’s or processor's environment. This type of tokenization is mainly used for recurring payments and subscription billing.
One-click payments
Merchants and payment processors exchange tokens that are generated when the consumer links their bank account with the merchant’s account. These tokens allow for identifying the consumer in the payment processor’s system. One-click payment tokenization is enabled by open banking and favoured by e-commerce companies serving returning customers.
Mobile payments
A single payment card can be digitalised into multiple independent payments through tokens. For example, one physical card can have separate tokens for different devices. This tokenization is mainly used for NFC mobile wallets such as Apple Pay or Android Pay.
Why is tokenization important for online merchants?
One of the main reasons tokenization is important for online merchants is security. Tokenization adds a layer of security to digital transactions. Online payment fraud is a common issue in the digital world, and online merchants are often the victims.
Another benefit is a smooth customer checkout experience. Companies with returning clients can improve their customer experience by offering an account linking feature. It enables consumers to shop in a single click, which provides them with a smooth and simplified checkout flow without compromising their data security.
Tokenization benefits
Using tokens for exchanging data has more benefits than just the obvious security advantage. Here are the main tokenization benefits for various companies and their consumers:
Increased conversions
The account linking feature is boosted with tokens, which ensures consumer data is securely saved for future shopping. This feature enables consumers to securely link their bank account to a merchant's online shop and pay for their orders in a single click. It may increase conversions since consumers can be sure their data is saved securely while enjoying a simple checkout process.
Business compliance
Using tokens reduces the scope of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance since merchants and other companies don’t store sensitive cardholder information, only its tokens. Ensuring that a company meets PCI compliance regulations may be costly, so partnering with a secure payment service provider can reduce compliance-related costs.
Security
As already mentioned, tokens are one of the main security features in the payment industry. If fraudsters steal tokens, criminals cannot link them to any valuable information because the information is securely stored in a separate server. In simple terms, stolen tokens would be useless to any fraudster who manages to get their hands on them.
What are the differences between tokenization and encryption?
The main difference between tokens and encrypted data is that tokens replace data with unrelated code, while encrypted data involves the use of an algorithm to temporarily encrypt the data.
Encryption uses cryptography to protect sensitive information by transforming it into code. Each symbol is replaced with another one using an encryption algorithm. When the data reaches its destination, it’s decrypted using a password or a key.
Encrypted code is reversible, while tokens cannot be tracked to their origin using an algorithm. The PCI Security Standards Council views encryption as sensitive and applies more expensive compliance obligations to companies that choose encryption over tokenization.
However, encryption is one of the strongest card protection options for when the card is present. Meanwhile, tokenization is a more secure option for cardless payments. For maximum security, some companies choose to adopt both encryption and tokenization.
kevin. tokens for conversion-boosting checkout
kevin. uses OAuth 2.0, which is the payment industry-standard protocol for authorization. All banking data that kevin. communicates to businesses is tokenized and therefore secure. Our tokenization process is simple for companies and doesn’t introduce any extra steps for the consumers in the checkout process. kevin. account linking feature can boost merchants’ conversion rates. It allows consumers to link their bank accounts and conveniently pay for goods and services in a single click.